Introduction
PHP is composed of a set of one or more functions. Functions divide large programs into smaller, easier to handle pieces. Each function normally performs one specific task. Functions are used to reduce the code in the programming i.e. reusability. Functions can be placed anywhere in a page. PHP has more than 700 built-in functions.
Types of Functions
In this article I will describe only three types of functions, which are as follows:
A Simple function does not take any arguments (parameters) or values. The function name should start with a letter or underscore (_), but not a number.
Syntax
function functionName()
{
message ;
}
Example
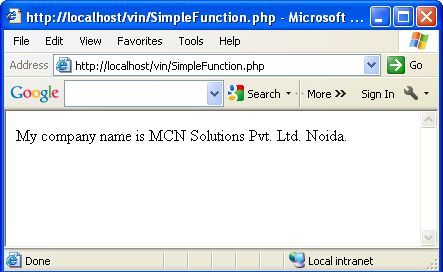
function CompnyName()
{echo "MCN Solutions Pvt. Ltd. Noida.";
} echo "My company name is ";
CompnyName();?>
Output
In the above example we build a CompnyName() function and print a message inside this function. This function is called later for printing the message.
Functions with Parameter
We can add arguments (parameters) to a function. Using parameters, we can add more functionally to a function. An argument is just like a variable of PHP. An argument (parameter) is specified inside the parenthesis of a function.
Syntax
function functionName (argument1,argument2)
{
message ;
}
Example1
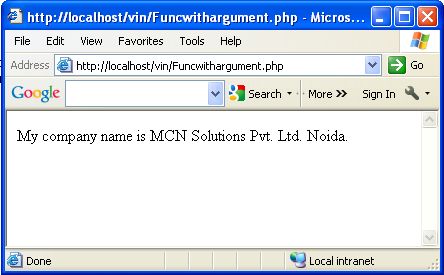
function CompnyName ($fullname) // one argument i.e. $fullname
{
echo $fullname;
}
echo "My company name is ";
CompnyName ("MCN Solutions Pvt. Ltd. Noida.");
?>
 Functions with Return values
Functions with Return values
In these types of functions, a function returns some values through the argument (parameter). Remember that a function should return at least one value.
Example1
function sum ($X, $Y)
{
$Z=$X + $Y;
return $Z;
}
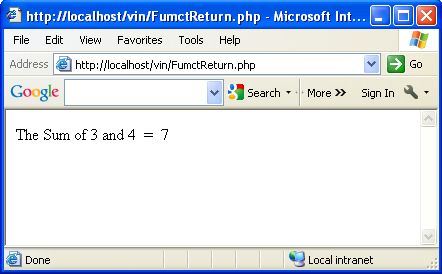
echo "The Sum of 3 and 4 = ".sum(3,4);
?>
Output
In the above example we build a sum() function and pass two arguments as $X and $Y. Now we declare a variable $Z, which takes a sum of $X and $Y then we will return $Z. Which shows the sum of X and y. In the above function we passed 3 and 4, which take by $X and $Y and returns the sum of these value to the variable $Z.
Example2
function sum ($X, $Y)
{
$Z=$X + $Y;
return $Z;
}
$X=5;
$Y=7;
$Sum=sum ($X,$Y); // assign the value of Z to $Sum
echo "The Sum of 5 and 7 = ".$Sum;
?>
Output
In the above example we build a sum() function and pass two arguments as $X and $Y. Now we declare a variable $Z, which takes to sum of $X and $Y then we will return $Z. Which shows the sum of X and y. In this example we assigned the value to $X and $Y i.e. 5 and 7 respectively. The sum of these values are returned by $Z to the $sum.
Conclusion
So in this article you saw types of functions and the use of functions in PHP. Using this article one can easily understand the concept of functions in PHP
PHP is composed of a set of one or more functions. Functions divide large programs into smaller, easier to handle pieces. Each function normally performs one specific task. Functions are used to reduce the code in the programming i.e. reusability. Functions can be placed anywhere in a page. PHP has more than 700 built-in functions.
Types of Functions
In this article I will describe only three types of functions, which are as follows:
- Simple Functions
- Functions with Parameter
- Functions with Return values
A Simple function does not take any arguments (parameters) or values. The function name should start with a letter or underscore (_), but not a number.
Syntax
function functionName()
{
message ;
}
Example
function CompnyName()
{echo "MCN Solutions Pvt. Ltd. Noida.";
} echo "My company name is ";
CompnyName();?>
Output
In the above example we build a CompnyName() function and print a message inside this function. This function is called later for printing the message.

Functions with Parameter
We can add arguments (parameters) to a function. Using parameters, we can add more functionally to a function. An argument is just like a variable of PHP. An argument (parameter) is specified inside the parenthesis of a function.
Syntax
function functionName (argument1,argument2)
{
message ;
}
Example1
function CompnyName ($fullname) // one argument i.e. $fullname
{
echo $fullname;
}
echo "My company name is ";
CompnyName ("MCN Solutions Pvt. Ltd. Noida.");
?>
Output
In
the above example we build a CompnyName() function and pass an argument
as a $fullname. This argument shows the message when you write a
message in this function.

Example2
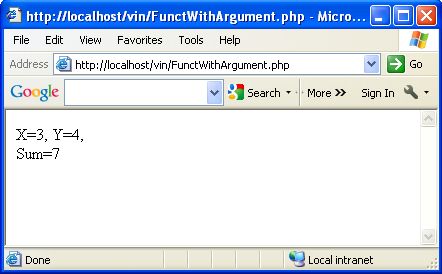
function sum ($X, $Y) // two argument i.e. $X and $Y
{
$Z=$X + $Y;
echo "X=$X, Y=$Y,
Sum=$Z ";
}
sum(3,4);
?>
function sum ($X, $Y) // two argument i.e. $X and $Y
{
$Z=$X + $Y;
echo "X=$X, Y=$Y,
Sum=$Z ";
}
sum(3,4);
?>
Output
In
the above example we build a sum() function and pass two arguments as
$X and $Y. These arguments i.e. $X and $Y takes the values, when you
pass the values in this function.

In these types of functions, a function returns some values through the argument (parameter). Remember that a function should return at least one value.
Example1
function sum ($X, $Y)
{
$Z=$X + $Y;
return $Z;
}
echo "The Sum of 3 and 4 = ".sum(3,4);
?>
Output
In the above example we build a sum() function and pass two arguments as $X and $Y. Now we declare a variable $Z, which takes a sum of $X and $Y then we will return $Z. Which shows the sum of X and y. In the above function we passed 3 and 4, which take by $X and $Y and returns the sum of these value to the variable $Z.

Example2
function sum ($X, $Y)
{
$Z=$X + $Y;
return $Z;
}
$X=5;
$Y=7;
$Sum=sum ($X,$Y); // assign the value of Z to $Sum
echo "The Sum of 5 and 7 = ".$Sum;
?>
Output
In the above example we build a sum() function and pass two arguments as $X and $Y. Now we declare a variable $Z, which takes to sum of $X and $Y then we will return $Z. Which shows the sum of X and y. In this example we assigned the value to $X and $Y i.e. 5 and 7 respectively. The sum of these values are returned by $Z to the $sum.

Conclusion
So in this article you saw types of functions and the use of functions in PHP. Using this article one can easily understand the concept of functions in PHP
No comments:
Post a Comment